How DevSpace Deploys Workspaces
Devspace deploys workspaces using the "up" command, when executed DevSpace builds a devcontainer, if not already available, then uses the provider to deploy the devcontainer to a workspace. Below is a sequence diagram of the main stages of the "up" command.
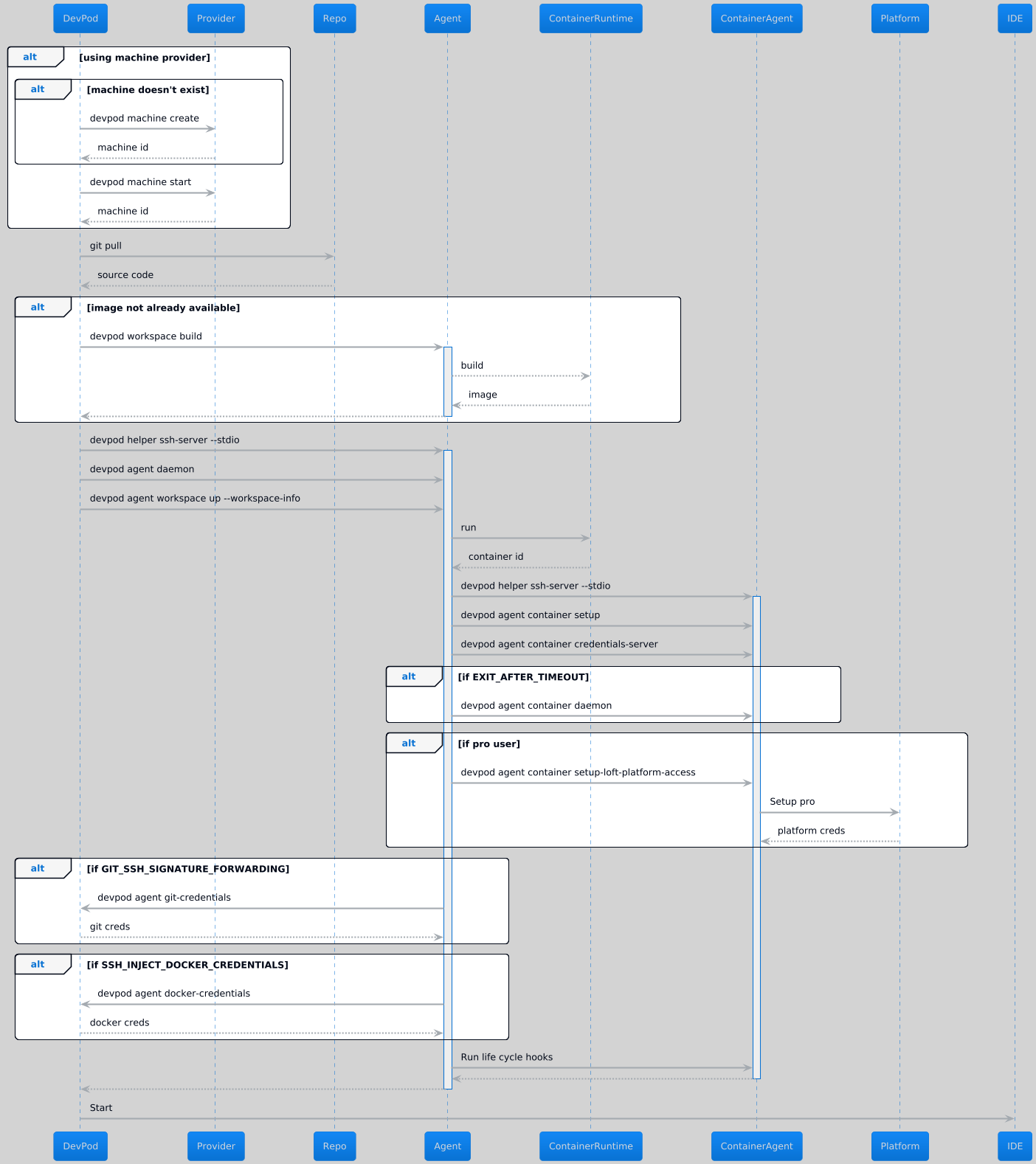
First DevSpace checks if we need to create/start a machine to deploy the devcontainer to. Next we pull the source code and .devcontainer.json source from git or a local file and use this with the local environment
to build the workspace. Building is done by the agent since we need access to build tools such as buildkit or kaniko, i.e. devspace workspace build. The workspace now contains everything needed,
so DevSpace sets up a SSH connection to the DevSpace agent running alongside the container's control plane.
The agent recieves "devspace agent workspace up" with the workspace spec serialised as workspace-info and uses the control plane (kube api server for k8s, docker daemon for anything else) to start the devcontainer. Once started DevSpace deploys a daemon to monitor activity, optionally sets up any platform access for pro users then optionally retrieves credentials from the local environment before launching the IDE. Once the IDE has started the deployment process has complete, DevSpace's agent daemon will continue to monitor the pod, if deployed, to put the machine or container to sleep when not in use.